ADHD Employment Statistics | Update 2024
Attention Deficit and Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a mental condition that affects millions of people in the United States. According to the National Institute of Mental Health, approximately 6.1 million children aged between 2 and 17 years old have been diagnosed with ADHD.
This is almost 10% of children in this age group in the country. As these children grow up and enter the workforce, they face a variety of challenges related to their condition.
In this article, we will explore the employment outlook for people with ADHD in the United States by looking at statistics related to their employment and unemployment rates, the best workplaces for people with ADHD, and more.
In this intellectual disability employment statistic roundup, you’ll learn:
–Employment Statistics for People with ADHD in the US
–Unemployment Statistics for People with ADHD in the US
–Most Common Reasons for a Higher Unemployment Rate
–Workplaces Environments for People with ADHD in the US
–Discrimination in the Workplace
–Accommodations for People with ADHD in the US
–Revealing ADHD at Work: Positive Impact on Work Experience
Editor’s Pick
- Approximately 6.1 million children aged 2-17 years old have been diagnosed with ADHD in the United States.
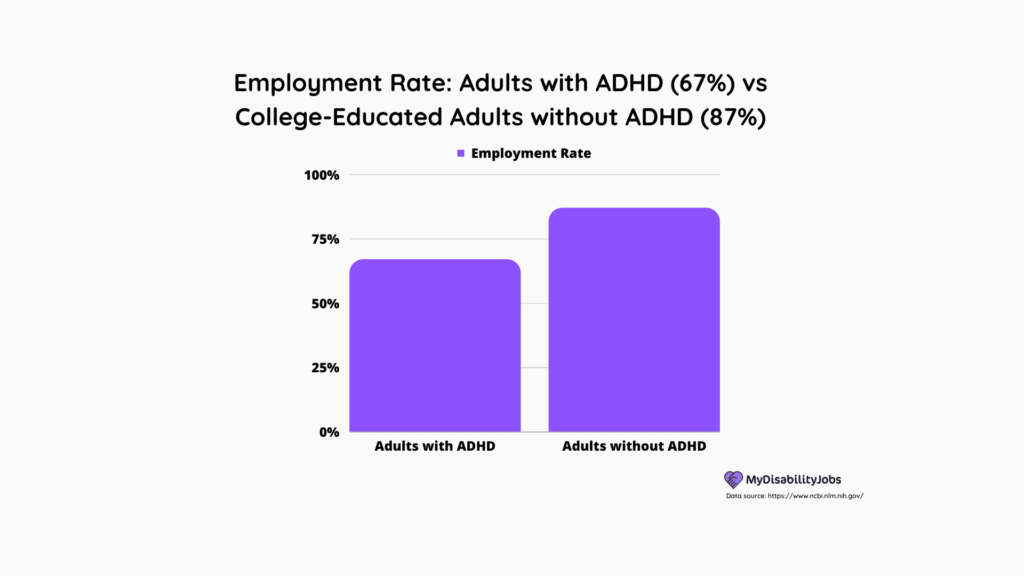
- The employment rate for adults with ADHD is 67%, whereas for adults without ADHD but with a college degree, it reaches as high as 87%.
- Adults with ADHD earn 17% less income than those without the condition.
- Adults with ADHD are less likely to be employed full-time compared to adults without ADHD (47% vs. 62%).
- Employees with ADHD are less likely to receive promotions compared to their peers without mental health conditions.
- Multitasking, creativity, and problem-solving jobs are the best fits for people with ADHD.
Is your company offering suitable jobs for people with disabilities? As an employer, you can publish your job offers on MyDisabilityJobs and reach thousands of qualified candidates.
Employment Statistics for People with ADHD in the US
The employment rate for people with ADHD is much lower than the rate for people without the condition.
- The Journal of Attention Disorders found that only 67% of adults with ADHD were employed, compared to 87% of adults without ADHD.
- The National Institutes of Health (NIH) found that adults with ADHD were less likely to be employed full-time compared to adults without ADHD (47% vs. 62%).
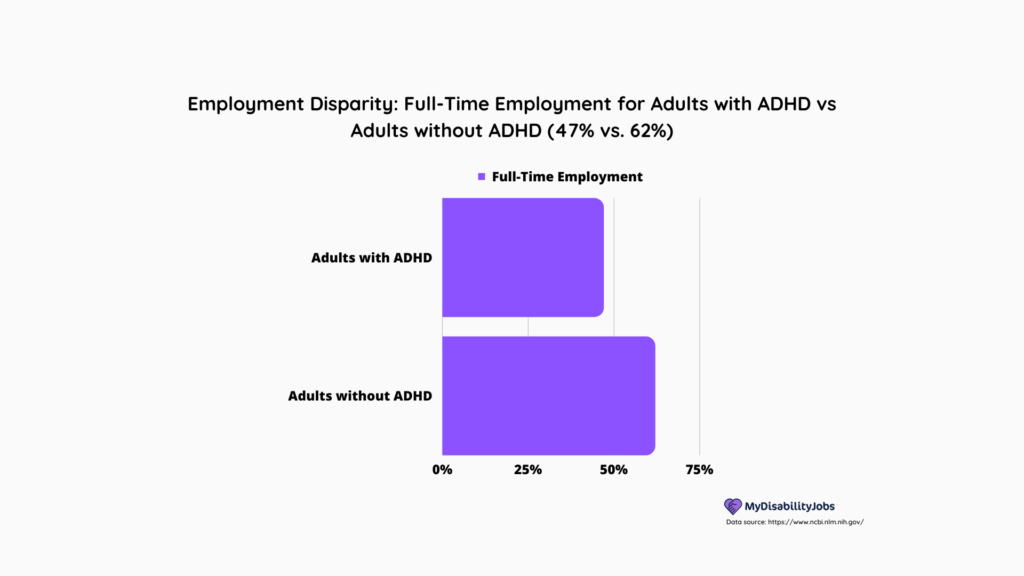
This represents a significant difference, and it highlights the challenges that individuals with ADHD face when it comes to finding and maintaining employment.
Adults with ADHD are more likely to be underemployed, which means that they work in jobs that are below their skill level or pay grade. This can have a significant impact on their earning potential and career advancement opportunities.
Source: National Library of Medicine, NLM.
Unemployment Statistics for People with ADHD in the US
In addition to facing challenges finding employment, people with ADHD are also more likely to experience unemployment.
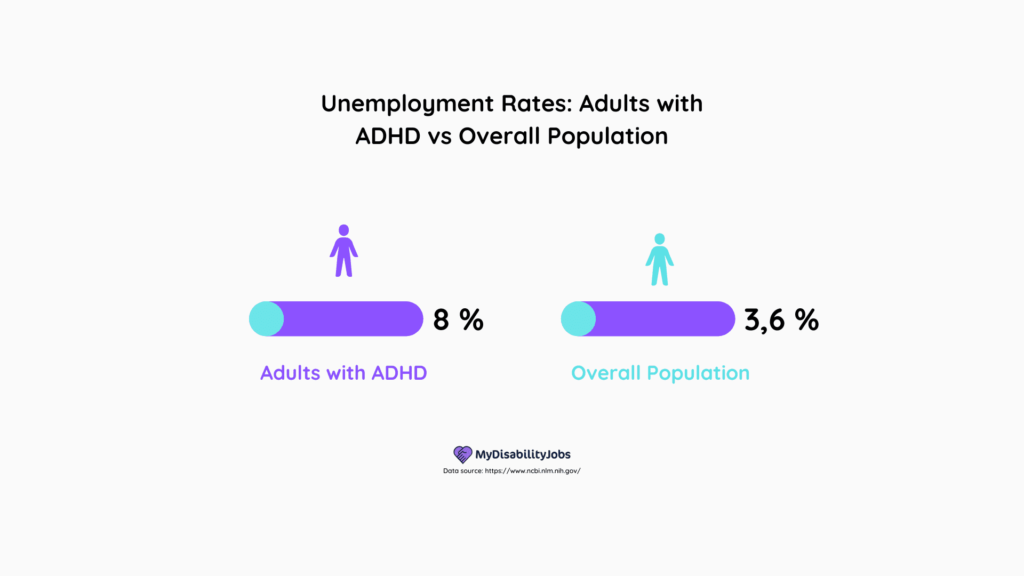
- The unemployment rate for adults with ADHD is approximately 8% which is significantly higher than the overall rates in the United States (3.6% in June 2023).
- Individuals who have completed high school and have ADHD tend to earn approximately 17% less compared to their counterparts without ADHD. Additionally, they also face a higher likelihood of experiencing periods of unemployment
In order to focus on what people with ADHD can do to fight these negative outlooks, is to understand that one of the reasons for this higher unemployment rate is their struggle with certain aspects of the job search process. For example, they may have difficulty with resume writing, job interviews, and networking. These challenges can make it harder for them to land a job, even if they are qualified and capable.
Most Common Reasons for a Higher Unemployment Rate
- Difficulty with organization and attention to detail: Individuals with ADHD may struggle with organizing their thoughts and presenting information clearly and concisely. This can make it challenging to create a well-structured and effective resume that highlights their skills and experience. Additionally, during job interviews, individuals with ADHD may struggle to stay focused and may have difficulty recalling important details.
- Impulsivity and hyperactivity: These treats can make it difficult to engage in effective networking. They may interrupt others or need help to listen attentively, which can make it challenging to make professional connections.
- Time management and planning: Individuals with ADHD may also struggle with time management and planning, which can make it challenging to meet deadlines and stay on top of job search activities. They may have difficulty prioritizing tasks and may become overwhelmed with the job search process, which may be overwhelmed by its nature.
Another reason for the higher unemployment rate among individuals with ADHD is that they may struggle with certain job requirements. For example, they may have difficulty with tasks that require sustained attention, focus, and organization. It can prevent them from applying to jobs with such requirements or make it harder for them to perform well on the job, leading to termination or resignation.
But there are always solutions to all those obstacles. Keep reading as we will discuss some resources further.
Source: NLM, Bureau of Labor Statistics.
Workplaces Environments for People with ADHD in the US
People with ADHD are employed in a wide range of industries and workplaces, but some environments may be better suited to their needs than others. For example, individuals with ADHD may struggle in jobs that require a lot of repetitive tasks or that do not offer much variety in their daily tasks.
According to the National Resource Center on ADHD, some workplaces that may be a good fit for individuals with ADHD include those that require multitasking, creativity, and problem-solving skills. Examples of such workplaces may include entrepreneurship, sports, the arts, technology, and marketing.
However, instead of a specific field of work, research has shown that workplaces that prioritize certain accommodations and work styles may be more conducive to the success of adults with ADHD.
The most suitable work styles for people with ADHD are:
- Flexible work arrangements: A study found that individuals with ADHD who worked in jobs with flexible schedules reported higher job satisfaction compared to those in jobs with rigid schedules.
- Remote work: A survey by FlexJobs found that 95% of respondents with ADHD reported that remote work would be beneficial for them, as it provides a less distracting and more controlled work environment.
- Collaborative work environments and job variety: The Journal of Occupational Health Psychology found that workers with ADHD in jobs with more collaborative work environments and job variety reported higher job satisfaction and better task performance.
- Open communication: Adults with ADHD who worked in jobs with open communication and supportive supervisors reported less job stress and better job performance.
While these statistics suggest that certain work arrangements and environments may be beneficial for workers with ADHD, it is important to note that accommodations should be made on a case-by-case basis. People with ADHD have different and unique needs and preferences, therefore, it is important for employers to work with them to find the best accommodations to support their success in the workplace.
Source: ADHDatwork, FlexJobs, Journal of Occupational Health Psychology.
Discrimination in the workplace
Research indicates that people diagnosed with ADHD may face discrimination in hiring, promotions, and job retention. Let’s review the results of such research:
- Discrimination in hiring: A study by the National Institute of Mental Health found that people with depression or ADHD were less likely to be offered a job compared to individuals without a mental health condition.
- Discrimination in promotions: According to a report by the Partnership for Workplace Mental Health, employees with ADHD were less likely to receive promotions compared to their peers without mental health conditions.
- Job retention: A study by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration found that individuals with ADHD had a higher rate of job loss compared to people without a mental health condition.
- Stigma and stereotypes: Colleagues in the workplace may have assumptions about their abilities, reliability, and professionalism. Stigma and stereotypes can create a hostile work environment and limit opportunities for career advancement.
Nevertheless, discrimination and stigma against people with ADHD and other mental health conditions are illegal in the US and their rights are protected under the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) and other laws. Employers are required to provide reasonable accommodations to individuals with disabilities, including ADHD, to ensure equal employment opportunities.
Source: PubMed, Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration.
Accommodations for People with ADHD in the US
To help individuals with ADHD succeed in the workplace, accommodations may be necessary. These accommodations may include things like flexible work schedules, the ability to work remotely, and access to tools and resources that can help with organization and time management.
Under the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), employers must provide reasonable accommodations to individuals with disabilities, including ADHD.
Revealing ADHD at Work: Positive Impact on Work Experience
It is up to each person with ADHD to disclose their condition and request accommodations. This can be a difficult decision, as disclosing their condition can allow them to receive the accommodations they need to succeed in their job. On the other hand, there is still a stigma attached to mental health conditions, and individuals with ADHD may worry about how their disclosure will be perceived by their employers and colleagues.
- According to a survey, approximately 56% of individuals with ADHD have disclosed their condition to their employer. Of those who disclosed, 75% reported that their disclosure had a positive impact on their work experience.
However, it is important to note that disclosure is a personal decision, and people should weigh the pros and cons before deciding whether or not to disclose their condition.
Source: Attention Deficit Disorder Association (ADDA).
Is your company offering suitable jobs for people with disabilities? As an employer, you can publish your job offers on MyDisabilityJobs and reach thousands of qualified candidates.
Conclusion
Adults with ADHD face unique challenges when it comes to employment in the United States. They may struggle with certain aspects of the job search process and may require accommodations to succeed in the workplace. However, with the right resources and support, individuals with ADHD can overcome these obstacles and achieve success in their careers.
It is important for adults with ADHD to find a supportive workplace and understanding of their condition, and to request accommodations when necessary. Employers can also benefit from hiring individuals with ADHD, as they bring unique strengths and skills to the table. In addition, identifying the best jobs for people with ADHD can contribute to their success and job satisfaction. By creating a workplace that is welcoming to individuals with ADHD, employers can tap into this potential and improve their overall productivity and success.
Furthermore, employers must create a workplace culture that is inclusive and supportive of individuals with ADHD and other disabilities, taking into account both the best and worst jobs for people with ADHD. This can include providing training and education to managers and employees on how to interact with and support individuals with ADHD, as well as creating policies and procedures that address accommodations and anti-discrimination.
FAQ
The unemployment rate for adults with ADHD is approximately 8% which is significantly higher than the overall rates in the United States (3.6% in June 2023).
The employment rate for adults with ADHD is 67%, whereas for adults without ADHD but with a college degree, it reaches as high as 87%.
Related articles:
Diversity in the Tech Industry: Statistics
Costs of Bullying and Harassment in the Workplace
Workplace Bullying Statistics Research & Facts
Statistics of Diversity in the Workplace
Mental Health and Employment Statistics
Disability and Depression Statistics
Disability and Employment Discrimination Statistics
Bipolar Disorder and Employment Statistics

Comments are closed